Nama ERP REST API
Nama ERP provides a comprehensive REST API for performing CRUD operations on all system entities, with full OpenAPI 3.0 specification support for seamless integration with third-party systems.
For a fast introduction, watch this video: Nama ERP Rest API Introduction
API Browser Overview
The Nama ERP API Browser provides an interactive interface for exploring and testing all available REST APIs in your system.
Accessing the API Browser
The API Browser is available through multiple endpoints:
Main API Browser (Router Page)
http[s]://<server-ip-or-domain>/erp/browseapi/
This displays the main router page with links to different API sections.
Entity APIs Browser
http[s]://<server-ip-or-domain>/erp/browseapi/browseentitiesapi.html
Lists all available entity APIs with their Arabic and English names.
Special Purpose APIs Browser
http[s]://<server-ip-or-domain>/erp/browseapi/browsespecialpurposesapi.html
Lists specialized APIs for specific integrations (e.g., attendance machine synchronization).
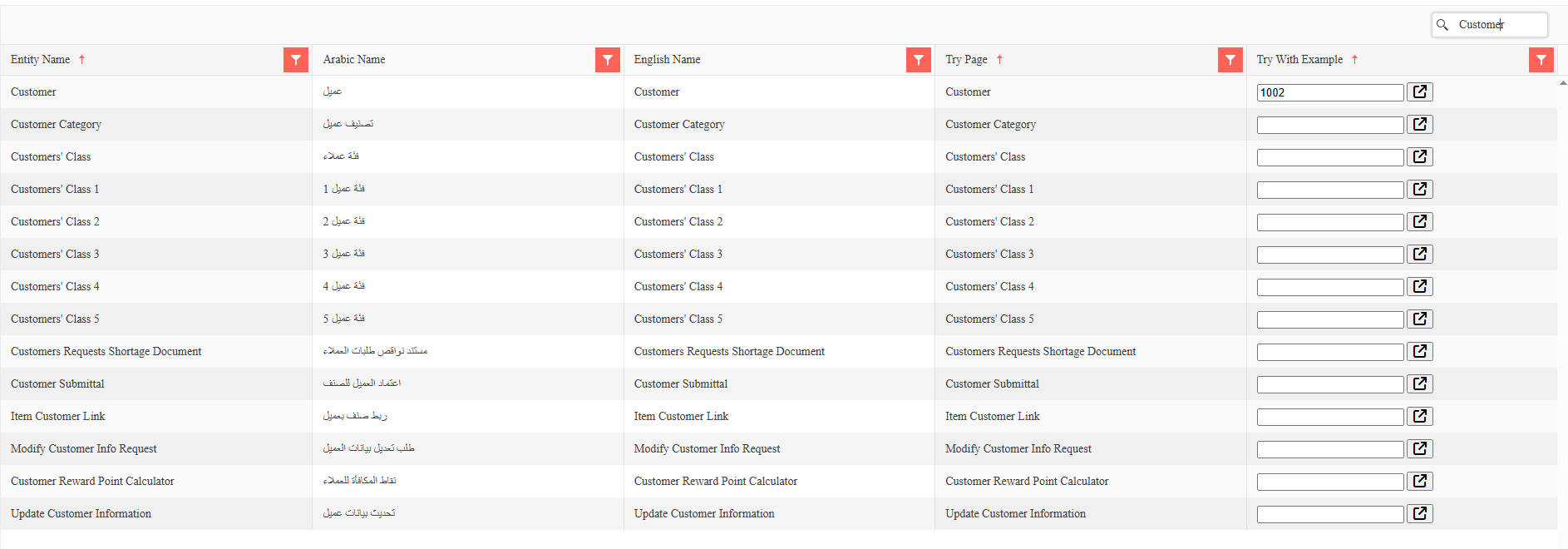
Features of the API Browser
The API Browser dynamically generates documentation based on your system configuration:
Entity List: Displays all entities available to the current user based on:
- Module permissions
- User access rights
- Enabled features
- Customer-specific configurations
Multilingual Support: Shows entity names in both Arabic and English
For each entity, two primary resources are provided:
- OpenAPI JSON Specification: Machine-readable API definition
- Swagger UI: Interactive documentation and testing interface
OpenAPI JSON Specifications
Basic OpenAPI Endpoint
http[s]://<server-ip-or-domain>/erp/browseapi/openapi/{EntityName}.json
OpenAPI with Example Data
http[s]://<server-ip-or-domain>/erp/browseapi/openapi/{EntityName}.json?exampleCode={code}
Parameters:
{EntityName}: The entity type (e.g., SalesInvoice, Customer, Item){code}: Optional - specific record code or UUID to use as example
Special Example Codes:
Find@First: Uses the first available record as example- Any valid business code or UUID from your system
Example URLs
# Get SalesInvoice OpenAPI spec with first available record
http://localhost:8080/erp/browseapi/openapi/SalesInvoice.json?exampleCode=Find@First
# Get Customer OpenAPI spec with specific customer
http://localhost:8080/erp/browseapi/openapi/Customer.json?exampleCode=CUST001
# Get Item OpenAPI spec without examples
http://localhost:8080/erp/browseapi/openapi/Item.json
API Response Structure
The OpenAPI specification includes detailed schema definitions for each entity:
Field Types Mapping
- String Fields: Text, BigText, Date, DateTime, Time, Email, Color, LatLng, Enum
- Number Fields: Decimal, Integer
- Boolean Fields: Boolean type fields
- Reference Fields: Returns the referenced entity's code
- Generic References: Object with
entityTypeandcodeproperties - Collections/Details: Arrays of objects (e.g., invoice lines, payment details)
Excluded Fields
The API automatically excludes:
- System-generated fields (unless specifically requested)
- Calculated fields
- Binary fields (images, documents)
- Internal user tracking fields
Working with Entity Collections
Many entities include detail collections (one-to-many relationships):
{
"invoiceLines": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"properties": {
"itemCode": { "type": "string" },
"quantity": { "type": "number" },
"unitPrice": { "type": "number" }
}
}
}
}
Collections represent detail records like:
- Invoice lines
- Payment lines
- Order items
- Journal entry lines
API Authentication & Access
Authentication Methods
Nama ERP REST API supports two authentication methods:
1. API Key Authentication (Recommended)
API Keys are the primary authentication method for production integrations.
Header-based Authentication:
apiKey: {your-api-key}
Query Parameter Authentication (Testing Only):
http://localhost:8080/erp/browseapi/openapi/SalesInvoice.json?apiKey={your-api-key}
Warning
Query parameter authentication should only be used for testing in the API Browser. Production integrations must use header-based authentication for security.
2. Session-based Authentication
For browser-based testing, you can use session cookies from a logged-in user session.
How to Generate an API Key
The system administrator can generate API keys using the API Credentials master screen:
- Open the API Credentials screen
- Create a new record with:
- Code: Unique identifier for this API credential
- Name: Descriptive name for the integration
- Select the User whose permissions will apply to this key
- Save the record
- Important: The API Key displays once after saving—copy it immediately
- Provide the key securely to the development/integration team
Permission Inheritance
The API Key inherits all access permissions from the selected user:
- Entity access rights
- Module permissions
- Data visibility rules
- Company/branch restrictions
Viewing API Keys After Creation
To view an API Key again after initial creation:
- Open the API Credentials record
- Check "View API Key" option
- Click Save
- The API Key will display on screen
Audit Trail
Re-exposing an API key is logged in the audit trail for security tracking.
API Key Best Practices
- Create separate keys for different integrations
- Use descriptive names to identify each integration
- Assign minimal permissions needed for each integration
- Rotate keys periodically for security
- Monitor API usage through audit logs
- Revoke unused keys to minimize security risks
CORS Configuration
The API Browser automatically handles Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) for API requests:
- Allows cross-origin requests from any domain (development mode)
- Supports preflight OPTIONS requests
- Includes necessary CORS headers in responses
Production CORS
In production environments, configure CORS policies to restrict access to specific domains for security.
REST API Endpoints
Base URL Structure
http[s]://<server>/erp/rest/v1/{entity}/{operation}/{idOrCode}
Path Parameters:
{entity}: Entity type name (e.g., Customer, SalesInvoice, Item){operation}: Operation to perform (findByIdOrCode, list, save, delete){idOrCode}: Optional - Entity UUID or business code
HTTP Methods Support
The API supports multiple HTTP methods for flexibility:
| HTTP Method | Supported Operations | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| GET | findByIdOrCode | Retrieve single entity by ID/code |
| POST | All operations | Universal method for all operations |
| PUT | save | Update existing entities |
| DELETE | delete | Remove entities |
RESTful Flexibility
While the API supports RESTful conventions, all operations can be performed using POST method for compatibility with various client implementations.
Supported Operations
1. Retrieve Entity (GET)
GET /erp/rest/v1/{entity}/findByIdOrCode/{idOrCode}
apiKey: {api-key}
responseFields: code,name1,contactInfo.email # Optional header/parameter
Batch Retrieval:
POST /erp/rest/v1/{entity}/findByIdOrCode
apiKey: {api-key}
Content-Type: application/json
["CUST001", "CUST002", "550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"]
2. List Entities with Pagination (POST)
POST /erp/rest/v1/{entity}/list
apiKey: {api-key}
Content-Type: application/json
{
"startPage": 1, # 1-based page number
"pageSize": 25, # Max 1000 records per page
"textCriteria": "status,Equal,Active,AND;city,Equal,Riyadh,AND;",
"orderBy": "creationDate:desc,code"
}
Response includes:
totalRecordsCount: Total matching recordsrecords: Array of requested recordsrecords_count: Number of records in response
3. Create/Update Entity (POST/PUT)
POST /erp/rest/v1/{entity}/save
apiKey: {api-key}
Content-Type: application/json
# Request Headers/Parameters:
saveAsDraft: false # Save as draft without validation
addRecord: true # Allow creating new records
updateRecord: true # Allow updating existing records
addToCurrentLines: false # Append to existing detail lines
trimExtraSpaces: false # Trim whitespace from strings
continueOnErrors: true # Continue processing on errors
useUserDimension: true # Apply user dimension filters
ignoredUnFoundRefs: false # Ignore missing references
responseFields: code,id # Fields to return after save
# Body: Entity data in JSON format
{
"code": "CUST001",
"name1": "Customer Name",
"contactInfo": {
"email": "customer@example.com",
"phone": "+966501234567"
},
"invoiceLines": [
{
"itemCode": "ITEM001",
"quantity": 5,
"unitPrice": 100
}
]
}
Response:
{
"saved_records_count": 1,
"saved_records": {
"Customer": [
{
"code": "CUST001",
"id": "550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"
}
]
}
}
4. Delete Entity (DELETE)
DELETE /erp/rest/v1/{entity}/delete/{idOrCode}
apiKey: {api-key}
Batch Deletion:
POST /erp/rest/v1/{entity}/delete
apiKey: {api-key}
Content-Type: application/json
["CUST001", "CUST002", "550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"]
Response:
{
"deleted_records_count": 2,
"deleted_records": ["CUST001", "CUST002"],
"failed_records_count": 1,
"failed_records": [
{
"entityType": "Customer",
"code": "550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000",
"indexInRequest": 2,
"errors": [
{
"message": "Record is referenced by other entities"
}
]
}
]
}
Testing APIs
Using the API Browser for Testing
The API Browser provides multiple ways to test APIs:
1. Direct OpenAPI JSON Access
# Get the OpenAPI spec with examples
curl -H "apiKey: {api-key}" \
"http://localhost:8080/erp/browseapi/openapi/Customer.json?exampleCode=Find@First"
2. Import to Postman
- Copy the OpenAPI JSON URL
- In Postman: Import → Link → Paste URL
- Add API Key to collection authentication
- Test all CRUD operations
3. Interactive Swagger UI
Access the Swagger interface for interactive testing (if configured).
Example Request Formats
Finding Single Record
GET /erp/rest/v1/Customer/findByIdOrCode/CUST001
apiKey: {api-key}
Finding Multiple Records
POST /erp/rest/v1/Customer/findByIdOrCode
apiKey: {api-key}
Content-Type: application/json
["CUST001", "CUST002", "CUST003"]
Creating New Record
POST /erp/rest/v1/Customer/save
apiKey: {api-key}
Content-Type: application/json
addRecord: true
updateRecord: false
{
"code": "CUST001",
"name1": "Customer Name",
"contactInfo": {
"email": "customer@example.com",
"phone": "+966501234567"
}
}
Updating Existing Record
POST /erp/rest/v1/Customer/save
apiKey: {api-key}
Content-Type: application/json
addRecord: false
updateRecord: true
{
"code": "CUST001",
"name1": "Updated Customer Name",
"contactInfo": {
"email": "newemail@example.com"
}
}
Listing with Filters
POST /erp/rest/v1/Customer/list
apiKey: {api-key}
Content-Type: application/json
{
"startPage": 1,
"pageSize": 50,
"textCriteria": "city,Equal,Riyadh,AND;status,Equal,Active,AND;",
"orderBy": "status,creationDate:desc,name1"
}
Error Handling
The API returns standard HTTP status codes and detailed error messages:
Common Response Codes
- 200 OK: Successful request
- 201 Created: Resource created successfully
- 400 Bad Request: Invalid request parameters
- 401 Unauthorized: Missing or invalid API key
- 403 Forbidden: Insufficient permissions
- 404 Not Found: Resource not found
- 500 Internal Server Error: Server-side error
Error Response Format
{
"error": {
"code": "ENTITY_NOT_FOUND",
"message": "Customer with code CUST999 not found",
"details": "Additional error information"
}
}
Special Purpose APIs
Beyond standard entity CRUD operations, Nama ERP provides specialized APIs:
Attendance Machine Integration
- Endpoint:
attcron-open-api-template - Purpose: Synchronize attendance data from biometric devices
- Supports batch processing of attendance records
Data Export API
- Export records as JSON with full relationship data
- Supports filtering and pagination
- Preserves data integrity for backup/migration
Batch Operations
- Process multiple records in single request
- Transactional processing with rollback on errors
- Optimized for high-volume integrations
Performance Considerations
Pagination
All list endpoints support pagination with configurable page size:
POST /erp/rest/v1/{entity}/list
Content-Type: application/json
{
"startPage": 1, # 1-based indexing
"pageSize": 50 # Maximum 1000 per request
}
Pagination Response:
{
"totalRecordsCount": 2547,
"records_count": 50,
"records": { ... }
}
Field Selection
Control which fields are returned to optimize payload size:
GET /erp/rest/v1/{entity}/findByIdOrCode/{code}
responseFields: code,name1,status,balance
Using responseFields parameter:
- Pass as HTTP header:
responseFields: field1,field2,field3 - Or as query parameter:
?responseFields=field1,field2,field3 - Supports nested fields:
contactInfo.email,address.city - Default fields if not specified:
code,id
Batch Operations
Process multiple records in a single request for better performance:
Batch Retrieval
POST /erp/rest/v1/Customer/findByIdOrCode
Content-Type: application/json
["CUST001", "CUST002", "550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000"]
Batch Import/Save
POST /erp/rest/v1/Customer/save
Content-Type: application/json
continueOnErrors: true
[
{
"code": "CUST001",
"name1": "Customer 1"
},
{
"code": "CUST002",
"name1": "Customer 2"
}
]
Query Criteria & Sorting
Use Nama ERP's structured text criteria format for filtering and sorting:
{
"textCriteria": "code,StartsWith,INV,AND;status,Equal,Active,AND;balance,GreaterThan,1000,AND;",
"orderBy": "status,creationDate:desc,code:asc"
}
Text Criteria Format: Each condition follows the pattern: fieldID,operator,value,logic;
Example Criteria:
code,StartsWith,01,AND;
name1,Contains,abc,AND;
date1,Equal,06-07-2025,AND;
creationDate,GreaterThanOrEqual,2025-07-06T13:05:00.000,AND;
amount,GreaterThan,1000,AND;
status,Equal,Active,OR;
type,In,Type1|Type2|Type3,AND;
Supported Operators:
- Equality:
Equal,NotEqual - Comparison:
GreaterThan,GreaterThanOrEqual,LessThan,LessThanOrEqual - Text Matching:
StartsWith,NotStartsWith,EndsWith,NotEndWith,Contains,NotContain - List Operations:
In,NotIn - Grouping:
OpenBracket,CloseBracket
Logical Relationships:
AND- All conditions must matchOR- At least one condition must match
Field Value Formats:
- Date Fields:
dd-MM-yyyy(e.g.,06-07-2025) - DateTime Fields:
yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.SSS(e.g.,2025-07-06T13:05:00.000) - Reference Fields:
id:entityType:codeor use.id/.codesuffix- Example:
customer.id,Equal,ffff0001-79e2-11f2-8800-0000ff79c2dd,AND; - Example:
customer.code,Equal,CUST001,AND;
- Example:
Building Criteria
Use the Criteria Definition screen in Nama ERP to visually build filter conditions, then click Convert to Text to get the text representation for API use.
Order By Format
Specify sort order for one or multiple fields using comma-separated values:
Format: fieldName:direction,fieldName2:direction,fieldName3
Examples:
- Multiple fields:
"orderBy": "code:desc,name1,creationDate:asc" - Single field:
"orderBy": "code:asc" - Default direction (ascending):
"orderBy": "name1,code" - Mixed directions:
"orderBy": "status,creationDate:desc,code:asc"
Direction Values:
:asc- Ascending order (A-Z, 0-9, oldest to newest) - default if omitted:desc- Descending order (Z-A, 9-0, newest to oldest)
Notes:
- Direction is optional; when omitted, defaults to ascending (
:asc) - Multiple fields are separated by commas
- Each field can have its own sort direction
- Duplicate fields are automatically filtered out
Import Options
Fine-tune import behavior with request headers:
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
saveAsDraft | false | Save without validation rules |
addRecord | true | Allow creating new records |
updateRecord | true | Allow updating existing records |
addToCurrentLines | false | Append to existing detail lines instead of replacing |
trimExtraSpaces | false | Remove leading/trailing whitespace |
continueOnErrors | true | Continue processing remaining records on error |
useUserDimension | true | Apply user's dimension filters |
ignoredUnFoundRefs | false | Skip validation of reference fields |
Troubleshooting
Common Issues and Solutions
API Key Not Working
- Verify key is active in API Credentials screen
- Check user permissions for the entity
- Ensure correct Authorization header format
Empty Example Data
- Verify records exist for the entity
- Check user data visibility permissions
- Use
Find@Firstto get any available record
Missing Fields in Response
- System fields excluded by default
- Binary fields not included in API responses
- Calculated fields not available via API